Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 3 - AWS Compute Services > Day 12 - EC2 Storage & Backup
Day 12 - EC2 Storage & Backup
Date: 2025-09-23 (Tuesday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
EC2 Storage & Security
Backup in EC2
- AWS Backup provides centralized backup for AWS services including EC2.
- EBS Snapshots back up EBS volumes:
- Point-in-time backups
- Incremental (stores only changed blocks)
- Stored in S3 (not directly accessible)
- AMI Backup captures the full EC2 configuration as an image.
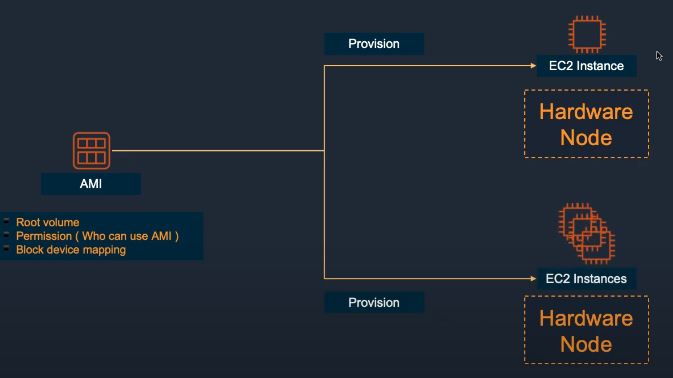
Snapshot Best Practices:
- Schedule regular snapshots
- Copy snapshots to other regions for DR
- Tag snapshots for lifecycle management
- Use Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM)
Key Pair
- Key Pairs are used for secure authentication when connecting to EC2:
- Public Key – stored on the instance
- Private Key – kept by the user for SSH (Linux) or RDP (Windows)
- Replaces passwords for better security.
- Important: If you lose your private key, AWS cannot recover it.
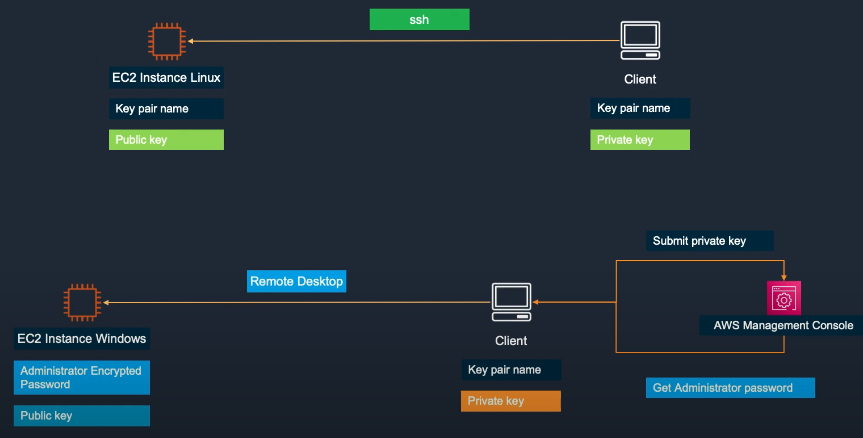
Key Pair Management:
- Create key pairs in AWS or import your own
- Store private keys securely
- Use different key pairs for different environments
- Rotate keys regularly
Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- Amazon EBS provides persistent block storage for EC2 instances.
- Volume types:
- General Purpose SSD (gp2/gp3) – balance between performance & cost
- Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1/io2) – for high IOPS workloads
- Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) – for large, sequential data
- Cold HDD (sc1) – low-cost, infrequently accessed data
Key Features
- Attach/detach volumes from instances
- Data persists when instances stop
- Create snapshots for backup or cross-region copy
- Automatically replicated within an AZ
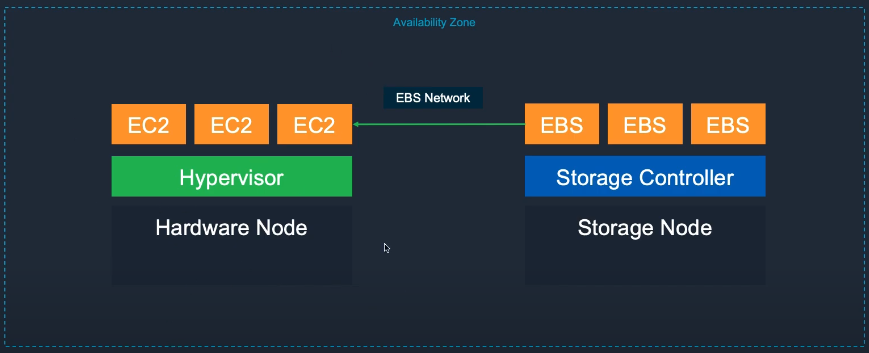
EBS Volume Comparison:
| Type | Use Case | Max IOPS | Max Throughput |
|---|---|---|---|
| gp3 | General purpose | 16,000 | 1,000 MB/s |
| io2 | High performance | 64,000 | 1,000 MB/s |
| st1 | Big data | 500 | 500 MB/s |
| sc1 | Cold storage | 250 | 250 MB/s |