Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 3 - AWS Compute Services > Day 13 - Instance Store & User Data
Day 13 - Instance Store & User Data
Date: 2025-09-24 (Wednesday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
EC2 Advanced Features
Instance Store
- Instance Store provides temporary block-level storage physically attached to the EC2 host.
Characteristics
- Very high I/O and throughput
- Data lost when instance stops or terminates
- Cannot be detached or snapshotted
Use Cases
- Caching or temporary data processing
- Applications with their own redundancy or replication
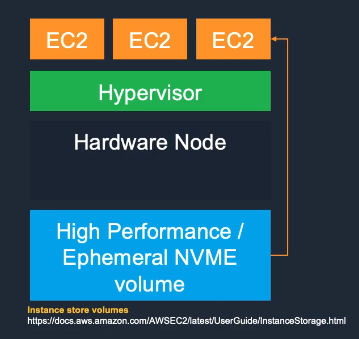
Instance Store vs EBS:
| Feature | Instance Store | EBS |
|---|---|---|
| Persistence | Temporary | Persistent |
| Performance | Very high | High |
| Snapshot | No | Yes |
| Detachable | No | Yes |
| Cost | Included | Additional |
User Data
- User Data scripts run automatically at instance launch (once per AMI provision).
- Linux – bash scripts
- Windows – PowerShell scripts
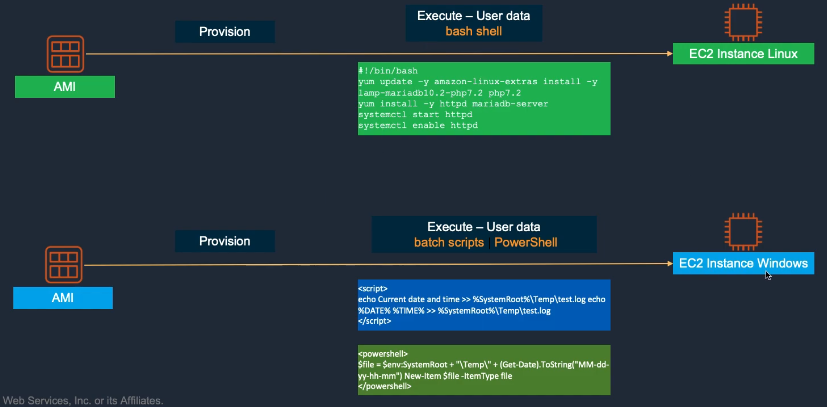
User Data Examples:
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
echo "<h1>Hello from $(hostname -f)</h1>" > /var/www/html/index.html
Metadata
- EC2 Instance Metadata provides details about the running instance such as private/public IP, hostname, and security groups.
- Often used in user data scripts for dynamic configuration.
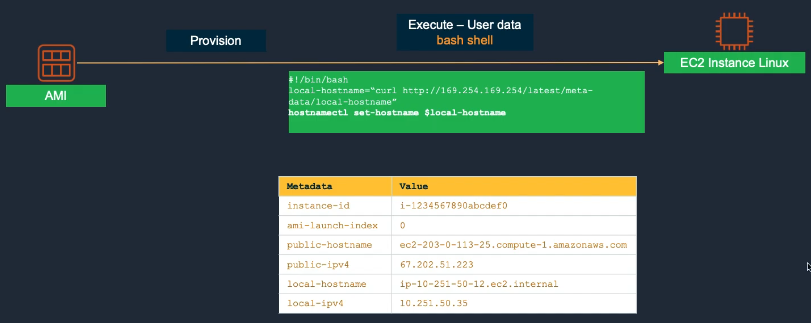
Accessing Metadata:
# Get instance ID
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id
# Get public IP
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4
# Get IAM role credentials
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/role-name
Hands-On Labs
Lab 07 – AWS Budgets & Cost Management
- Create Budget by Template → 07-01
- Create Cost Budget Tutorial → 07-02
- Create Usage Budget → 07-03
- Create Reserved Instance Budget → 07-04
- Create Savings Plans Budget → 07-05
- Clean Up Budgets → 07-06