Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 5 - AWS Security & Identity > Day 21 - Shared Responsibility & IAM Basics
Day 21 - Shared Responsibility & IAM Basics
Date: 2025-10-06 (Monday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
Security
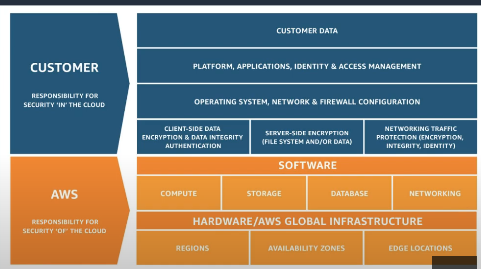
Shared Responsibility Model
- In cloud computing, security is a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the customer.
- Customers must securely configure services, apply best practices, and use security controls from the hypervisor exposure upward to application/data layers.
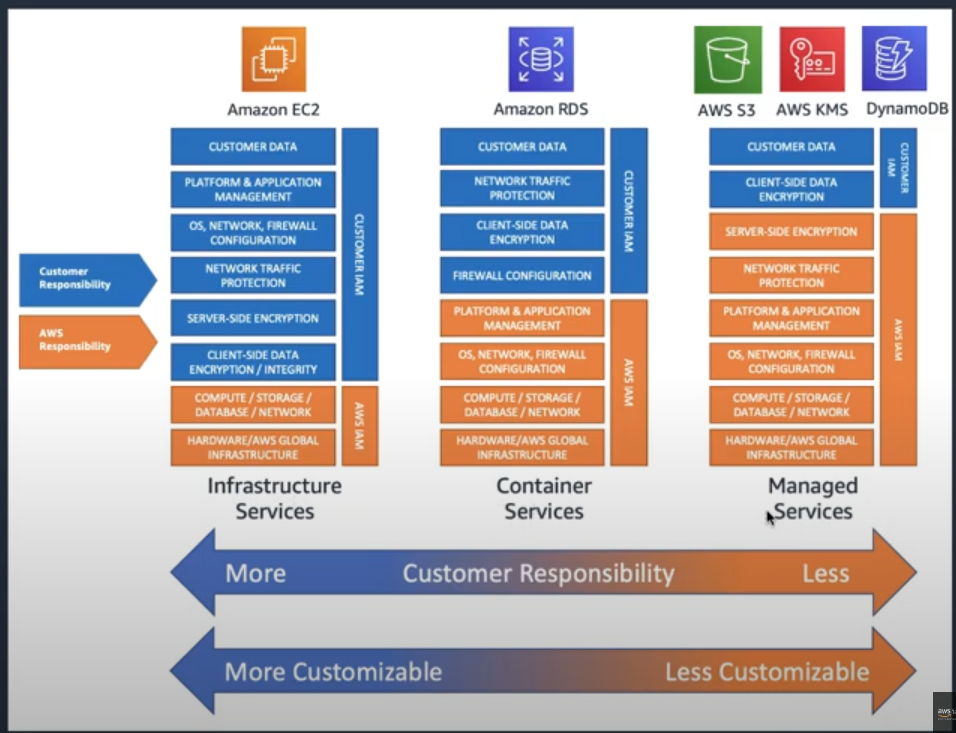
- The split of responsibilities varies by service model:
- Infrastructure-level services
- Partially managed services
- Fully managed services
AWS Responsibilities (Security OF the Cloud):
- Physical security of data centers
- Hardware and network infrastructure
- Virtualization infrastructure
- Managed service operations
Customer Responsibilities (Security IN the Cloud):
- Data encryption
- Network configuration
- Access management
- Application security
- Operating system patches (for EC2)
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Root Account
- Has unrestricted access to all AWS services/resources and can remove any attached permissions.
- Best practices:
- Create and use an IAM Administrator user for daily operations.
- Lock away root credentials (dual control).
- Keep the root user’s email and domain valid and renewed.
- Enable MFA on root account
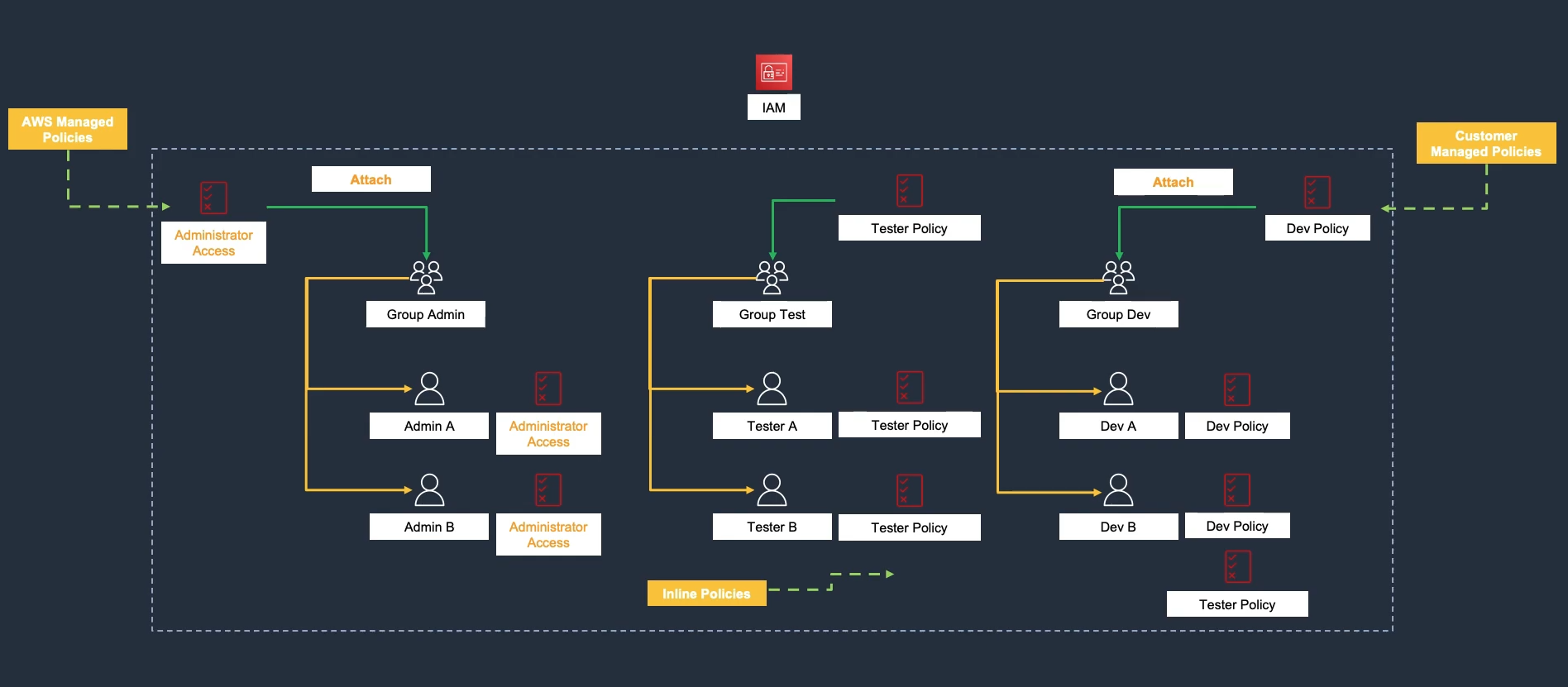
IAM Overview
- IAM controls access to AWS services and resources in your account.
- Principals include: root user, IAM users, federated users, IAM roles, assumed-role sessions, AWS services, and anonymous users.
- Notes:
- IAM users are not separate AWS accounts.
- New IAM users start with no permissions.
- Grant permissions by attaching policies to users, groups, or roles.
- Use IAM groups to manage many users (groups cannot be nested).
Hands-On Labs
Lab 48 – IAM Access Keys & Roles (Part 1)
- Create EC2 Instance → 48-1.1
- Create S3 Bucket → 48-1.2
- Generate IAM User and Access Key → 48-2.1