Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 6 - AWS Database Services > Day 26 - Database Fundamentals
Day 26 - Database Fundamentals
Date: 2025-10-13 (Monday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
Database Concepts Review
- A database is an organized (or semi-structured) collection of information stored on storage devices to support concurrent access by multiple users or programs with different goals.
Sessions
- A session spans from the moment a client connects to the DBMS until the connection is terminated.
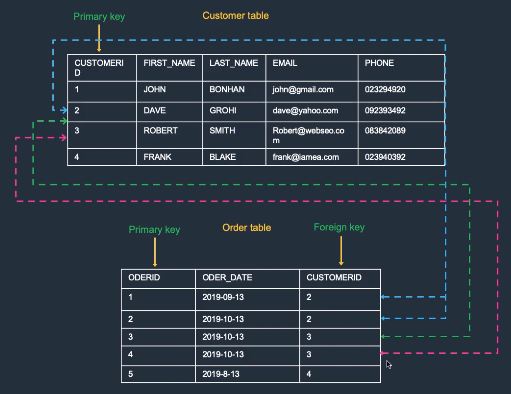
Primary Key
- A primary key uniquely identifies each row in a relational table.
Foreign Key
- A foreign key in one table references the primary key of another table, creating a relationship between them.
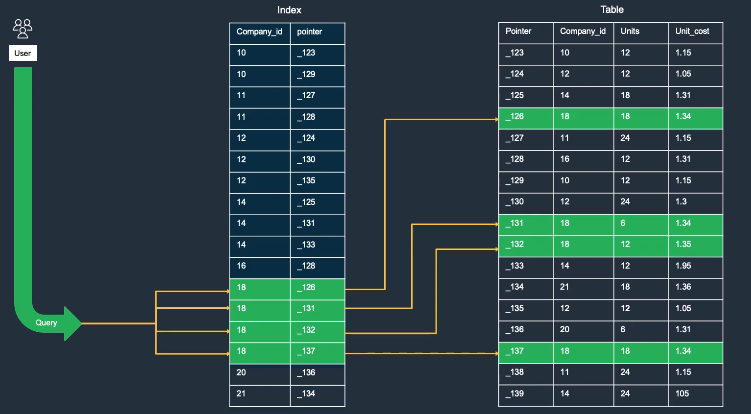
Index
- An index accelerates data retrieval at the cost of extra writes and storage to maintain the index structure.
- Indexes locate data without scanning every row; they can be defined over one or more columns.
Index Types:
- B-Tree: General purpose, balanced tree structure
- Hash: Fast equality lookups
- Bitmap: Efficient for low-cardinality columns
- Full-Text: Text search optimization
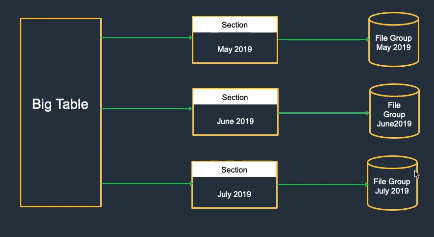
Partitioning
- Partitioning splits a large table into smaller, independent pieces (partitions), potentially placed on different storage.
- Benefits: better query performance, easier maintenance, and scalability.
- Common types:
- Range (e.g., by date)
- List
- Hash
- Composite (combination)
Partitioning Example:
-- Range partitioning by date
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
order_date DATE,
amount DECIMAL
) PARTITION BY RANGE (YEAR(order_date)) (
PARTITION p2023 VALUES LESS THAN (2024),
PARTITION p2024 VALUES LESS THAN (2025),
PARTITION p2025 VALUES LESS THAN (2026)
);
Execution Plan / Query Plan
- A query plan details how the DBMS will execute an SQL statement (access paths, joins, sorts).
- Types:
- Estimated plan (before execution)
- Actual plan (from executed query)
- Key operators: table scan, index seek/scan, nested loops, hash/merge join, sort, aggregate, filter.
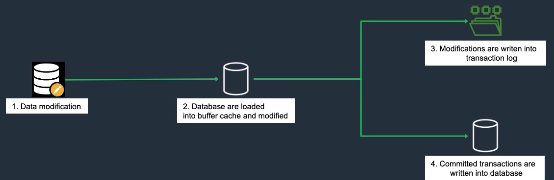
Database Logs
- Database logs record all changes (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) and operations.
- Typical log types: transaction, redo, undo, binary logs.
- Uses: recovery, integrity, consistency/durability (ACID), replication, performance analysis.
Buffers
- A buffer pool caches pages read from disk to minimize I/O.
- Management strategies:
- Replacement: LRU, FIFO, Clock
- Write policies: immediate vs. deferred
- Prefetching to warm the cache
Hands-On Labs
Lab 05 – Amazon RDS & EC2 Integration (Part 1)
- Create a VPC → 05-2.1
- Create EC2 Security Group → 05-2.2
- Create RDS Security Group → 05-2.3
- Create DB Subnet Group → 05-2.4