Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 6 - AWS Database Services > Day 27 - Amazon RDS & Aurora
Day 27 - Amazon RDS & Aurora
Date: 2025-10-14 (Tuesday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
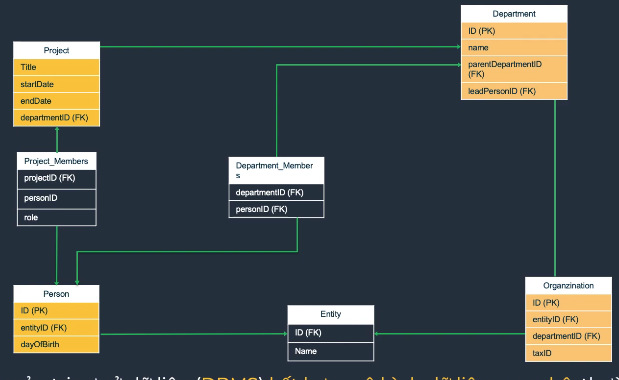
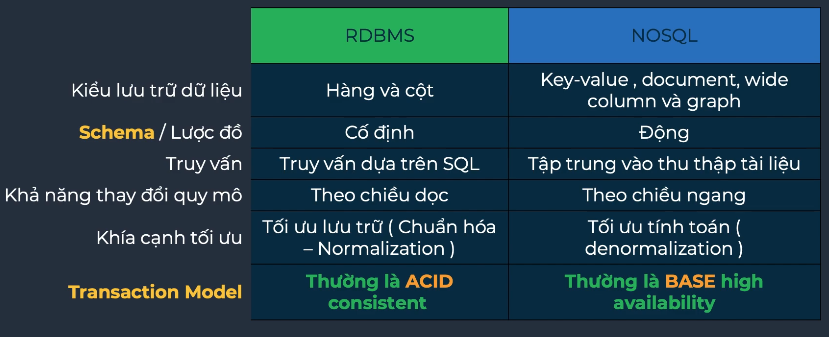
RDBMS vs NoSQL
RDBMS
- An RDBMS stores data in related tables (rows/columns), enforces integrity constraints, uses SQL, and provides ACID guarantees.
- Popular engines: Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, IBM Db2.
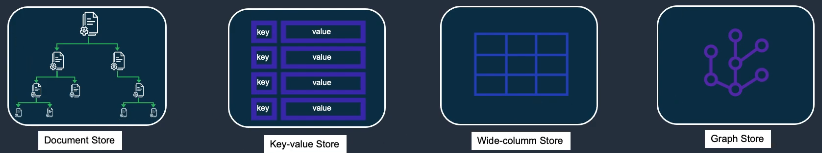
NoSQL Overview
- NoSQL systems target un/semistructured data with high scalability and performance.
- Types:
- Document (MongoDB, CouchDB)
- Key–Value (Redis, DynamoDB)
- Column-Family (Cassandra, HBase)
- Graph (Neo4j, Amazon Neptune)
- Traits: schema flexibility, horizontal scaling, big-data friendliness, CAP-oriented designs.
RDBMS vs. NoSQL (high-level)
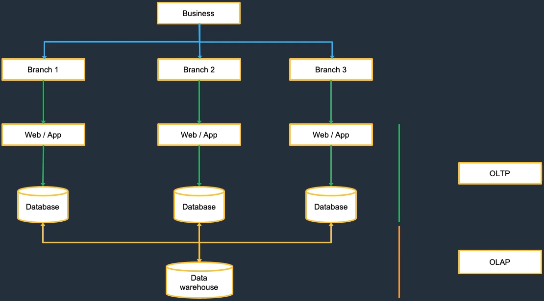
OLTP vs. OLAP
- OLTP: many small, concurrent transactions; normalized data; short queries; index-heavy.
- OLAP: complex analytics over large historical datasets; star/snowflake schemas; read-heavy.
Amazon RDS & Aurora
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
Managed relational databases that simplify provisioning, patching, backups, and HA.
- Supported engines: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server, Amazon Aurora.
- Key features: automated backups/patching, easy scaling, Multi-AZ high availability, encryption & VPC/IAM/SSL security.
- Deployment options:
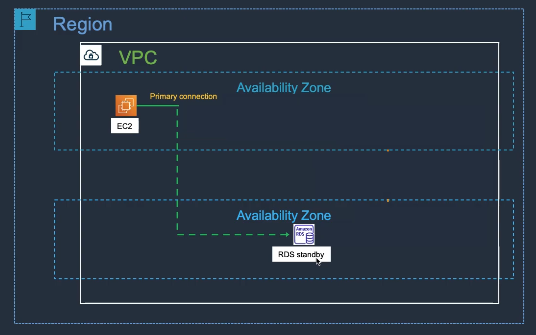
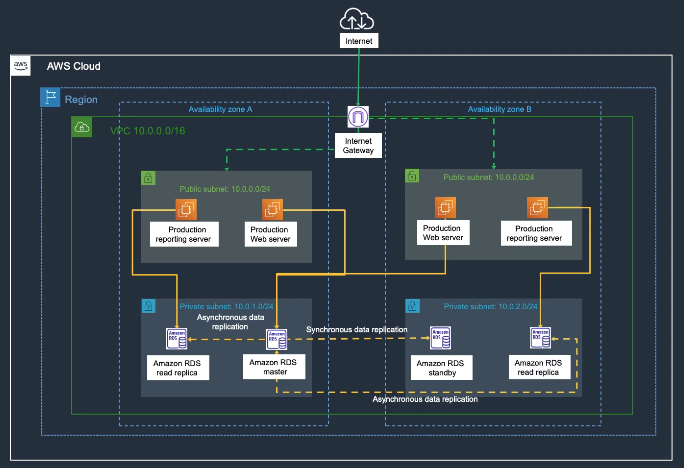
- Single-AZ
- Multi-AZ (synchronous standby in another AZ)
- Read Replicas for scaling reads
RDS Features:
- Automated Backups: Point-in-time recovery up to 35 days
- Manual Snapshots: User-initiated backups
- Multi-AZ: Automatic failover for high availability
- Read Replicas: Scale read workloads (up to 15 replicas)
- Parameter Groups: Database configuration management
- Option Groups: Additional features (e.g., Oracle Advanced Security)
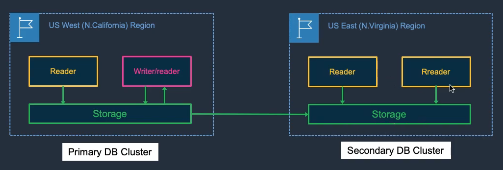
Amazon Aurora
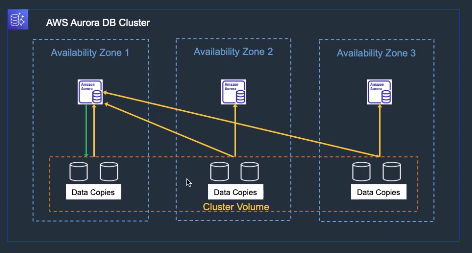
Cloud-native, MySQL/PostgreSQL-compatible relational database re-architected for AWS.
- Highlights:
- Up to ~5× MySQL / ~3× PostgreSQL performance (typical benchmarks)
- Storage auto-scales to 128 TB
- Six-way replication across three AZs; self-healing storage
- Aurora Serverless (on-demand capacity)
- Global Database for low-latency multi-region
Aurora Features:
- Aurora Replicas: Up to 15 read replicas with sub-10ms lag
- Aurora Serverless: Auto-scaling compute capacity
- Aurora Global Database: Cross-region replication < 1 second
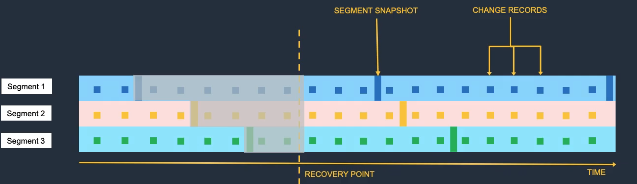
- Aurora Backtrack: Rewind database to specific point in time
- Aurora Parallel Query: Faster analytics on current data
- Aurora Machine Learning: Native ML integration
Aurora vs RDS:
| Feature | Aurora | RDS |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | 5x MySQL, 3x PostgreSQL | Standard |
| Storage | Auto-scaling to 128 TB | Manual scaling |
| Replicas | Up to 15 | Up to 5 (MySQL) |
| Failover | < 30 seconds | 1-2 minutes |
| Backtrack | Yes | No |
Hands-On Labs
Lab 05 – Amazon RDS & EC2 Integration (Part 2)
- Create EC2 Instance → 05-3
- Create RDS Database Instance → 05-4
- Application Deployment → 05-5
- Backup and Restore → 05-6
- Clean Up Resources → 05-7
Lab 43 – AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) (Part 1)
- EC2 Connect RDP Client → 43-01
- EC2 Connect Fleet Manager → 43-02
- SQL Server Source Config → 43-03
- Oracle Connect Source DB → 43-04
- Oracle Config Source DB → 43-05
- Drop Constraint → 43-06