Internship Report > Worklog - AWS Learning Journey > Week 6 - AWS Database Services > Day 28 - Amazon Redshift
Day 28 - Amazon Redshift
Date: 2025-10-15 (Wednesday)
Status: “Done”
Lecture Notes
Amazon Redshift
Fully managed cloud data warehouse optimized for large-scale analytics (OLAP).
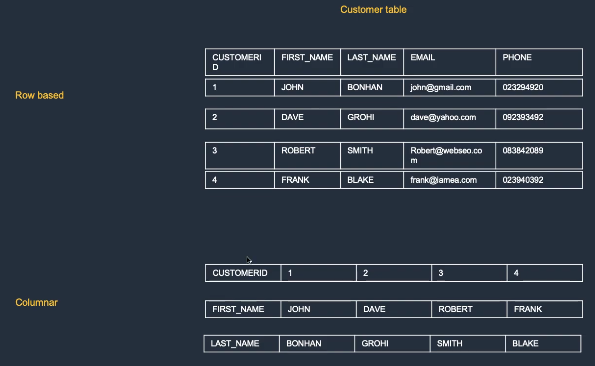
- Columnar storage, compression, MPP execution; scales from hundreds of GB to PB.
- Integrations: S3, Kinesis, DynamoDB, BI tools; strong security features.
- Concurrency Scaling adds capacity automatically during spikes.
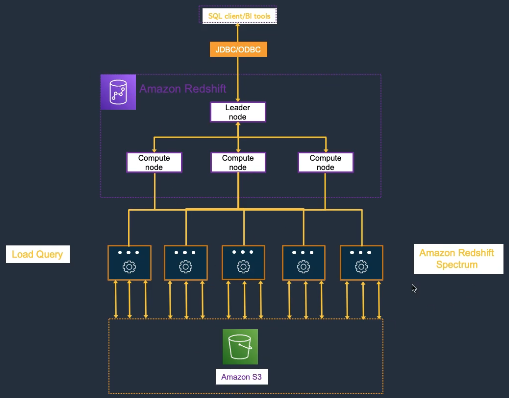
- Architecture: cluster (leader node + compute nodes), each compute node has slices.
Deployment options:
- Redshift Provisioned
- Redshift Serverless
- Redshift Spectrum (query S3 directly)
Use cases: enterprise BI, data lake analytics, dashboards, trend analysis, forecasting.
Redshift Features:
- Columnar Storage: Optimized for analytics queries
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP): Distributes queries across nodes
- Result Caching: Speeds up repeated queries
- Automatic Compression: Reduces storage costs
- Workload Management (WLM): Query prioritization
- Concurrency Scaling: Handle burst workloads
Redshift vs Traditional Data Warehouse:
| Feature | Redshift | Traditional DW |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Minutes | Weeks/Months |
| Scaling | Elastic | Fixed capacity |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go | Large upfront |
| Maintenance | Managed | Self-managed |
Redshift Spectrum:
- Query data directly in S3 without loading
- Separate compute and storage
- Support for various file formats (Parquet, ORC, JSON)
- Cost-effective for infrequently accessed data
Hands-On Labs
Lab 43 – AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) (Part 2)
- MSSQL → Aurora MySQL Target Config → 43-07
- MSSQL → Aurora MySQL Create Project → 43-08
- MSSQL → Aurora MySQL Schema Conversion → 43-09
- Oracle → MySQL Schema Conversion (1) → 43-10
- Create Migration Task & Endpoints → 43-11